참고도서: 이것이 자바다 (한빛미디어)
www.yes24.com/Product/Goods/15651484
이것이 자바다
15년 이상 자바 언어를 교육해온 자바 전문강사의 노하우를 아낌 없이 담아낸 자바 입문서. 저자 직강의 인터넷 강의와 Q/A를 위한 커뮤니티(네이커 카페)까지 무료로 제공하여 자바 개발자로 가
www.yes24.com
1. 조건문
1) if문
(1) if문 하나로 true가 될 때 실행, false가 되면 실행하지 않는 문장
(2) if ~ else문: true가 되면 if문을, false가 되면 else문을 실행
(3) if ~ else if ~ else문: 조건식이 3개 이상일 때에 사용
(4) 중첩 if문: if문 안에 if문을 넣을 때 사용
[예제1: if/else if/else문]
package com.hb.ch04;
public class IfElseIfExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = 75;
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("점수가 90보다 큽니다.");
System.out.println("등급은 A 입니다.");
} else if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("점수가 80~89 입니다.");
System.out.println("등급은 B 입니다.");
} else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("점수가 70~79 입니다.");
System.out.println("등급은 C 입니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("점수가 70보다 작습니다.");
System.out.println("등급은 D 입니다.");
}
}
}
[실행결과] - 75점에 대한 결과

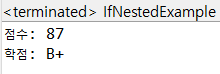
[예제2: 중첩 if문(Nested if)]
package com.hb.ch04;
public class IfNestedExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score = (int)(Math.random()*20) + 71;
System.out.println("점수: " + score);
String grade;
if(score >= 90) {
if(score >= 95) {
grade = "A+";
} else {
grade = "A";
}
} else if(score >= 80) {
if(score >= 85) {
grade = "B+";
} else {
grade = "B";
}
} else {
if(score >= 75) {
grade = "C+";
} else {
grade = "C";
}
}
System.out.println("학점: " + grade);
}
}
[실행결과] - 값은 랜덤으로 출력
2) switch문 - 조건 제어문
(1) Switch문: 괄호 안의 값과 동일한 값을 갖는 case로 가서 실행문을 실행
(2) break문이 없는 case: break가 없다면 다음 case가 연달아 실행
(3) char 타입의 Switch문: char 등 정수 타입 변수도 switch문에 사용 가능
(4) String 타입의 Switch문: Java 7부터 String 타입의 변수도 올 수 있음
[예제1: Switch문을 통한 주사위 번호 뽑기]
package com.hb.ch04;
public class SwitchControlStructure {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = (int) (Math.random() * 6) + 1;
switch (num) {
case 1:
System.out.println("1번이 나왔습니다.");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("2번이 나왔습니다.");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("3번이 나왔습니다.");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("4번이 나왔습니다.");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("5번이 나왔습니다.");
break;
default:
System.out.println("6번이 나왔습니다.");
break;
}
}
}
[실행결과]

[예제2: break가 없는 switch~case]
package com.hb.ch04;
public class SwitchNoBreakCaseExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//8<= … < 12(8+4) 사이의 정수 얻기
int time = (int)(Math.random()*4) + 8;
System.out.println("[현재시간: " + time + " 시]");
switch(time) {
case 8:
System.out.println("출근합니다.");
case 9:
System.out.println("회의를 합니다.");
case 10:
System.out.println("업무를 봅니다.");
default:
System.out.println("외근을 나갑니다.");
}
}
}
[실행결과]

2. 반복문
1) for문: 똑같은 실행문을 정해진 횟수만큼 반복적으로 실행
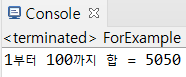
(1) 1부터 100까지의 합을 출력하는 예제
package com.hb.ch04;
public class ForExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i=1; i<=100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1부터 " + (i-1) + "까지 합 = " + sum);
}
}
(2) float 타입 카운터 변수 예제
package com.hb.ch04;
public class ForExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (float x = 0.1f; x <= 1.0f; x += 0.1f) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}

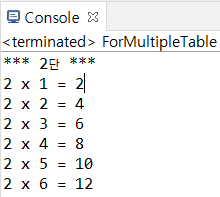
(3) 구구단 출력예제
package com.hb.ch04;
public class ForMultipleTable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int m = 2; m <= 9; m++) {
System.out.println("*** " + m + "단 ***");
for (int n = 1; n <= 9; n++) {
System.out.println(m + " x " + n + " = " + (m * n));
}
}
}
}
2) while문: 조건식이 true일 경우 계속해서 반복
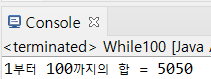
(1) 1부터 100까지의 합을 출력하는 예제
package com.hb.ch04;
public class While100 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while(i <= 100) {
sum += i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("1부터 " + (i-1) + "까지의 합 = " + sum);
}
}
(2) 각 키가 가지고 있는 키 코드(ASCII)를 이용한 while문 제어
: 0 = 48, 1 = 49, ..., 9 = 57 / A = 65, B = 66, ..., Z = 90, a = 91, ..., z = 122
Backspace = 8, Tab = 9, Enter = [CR=13, LF=10], ...
package com.hb.ch04;
public class WhileKeyControl {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
boolean run = true;
int speed = 0;
int keyCode = 0;
while(run) {
if(keyCode!=13 && keyCode!=10) {
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
System.out.println("1.증속 | 2.감속 | 3.중지");
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
System.out.print("선택: ");
}
keyCode = System.in.read();
if (keyCode == 49) { //1
speed++;
System.out.println("현재 속도=" + speed);
} else if (keyCode == 50) { //2
speed--;
System.out.println("현재 속도=" + speed);
} else if (keyCode == 51) { //3
run = false;
}
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
}

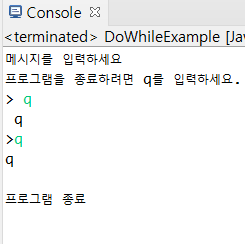
3) do-while문: 블록 내부의 실행문을 우선 실행시키고 실행 결과에 따라서 반복 실행을 계속할지 결정
package com.hb.ch04;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DoWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("메시지를 입력하세요");
System.out.println("프로그램을 종료하려면 q를 입력하세요.");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String inputString;
do {
System.out.print(">");
inputString = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println(inputString);
} while( ! inputString.equals("q") );
System.out.println();
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
scanner.close();
}
}
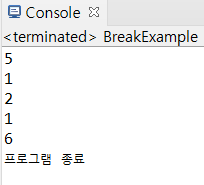
4) break문: 반복문을 실행 중지할 때 사용
package com.hb.ch04;
public class BreakExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
while(true) {
int num = (int)(Math.random()*6) + 1;
System.out.println(num);
if(num == 6) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
}
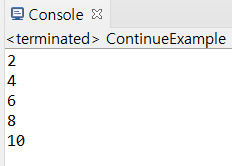
5) continue문: 반복문에서 for문의 증감식 또는 while문과 do-while문의 조건식으로 이동
package com.hb.ch04;
public class ContinueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) {
if(i%2 != 0) {
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
'데이터 [Data] > Java & JSP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 상속 (0) | 2021.04.29 |
|---|---|
| Scanner, Switch문을 활용한 사칙연산 계산기 (0) | 2021.04.29 |
| Scanner 클래스 예제 (0) | 2021.04.29 |
| 객체지향 프로그래밍(OOP; Object-Oriented Programming) (0) | 2021.04.28 |
| Java 프로그래밍 입문 및 환경설정 + 롬복 패키지 (0) | 2021.04.28 |




댓글